

Along the way Galileo performed close observation of the asteroids 951 Gaspra ( October 29, 1991) and 243 Ida, and discovered Ida's moon Dactyl. New safety protocols introduced as a result of the Challenger accident forced Galileo to use a lower-powered upper stage booster rocket, instead of a Centaur booster rocket, to send it from Earth orbit to Jupiter several gravitational slingshots (once by Venus and twice by Earth), called a "VEEGA" or Venus Earth Earth Gravity Assist maneuver, provided the additional velocity required to reach its destination. Galileo's launch had been significantly delayed by the hiatus in Space Shuttle launches that occurred after the Challenger space shuttle disaster. 6.4 Near failure of atmospheric probe parachute.6.2 Tape recorder anomalies and remote repair.5.4.2 Second asteroid encounter: 243 Ida and Dactyl.5.4.1 First asteroid encounter: 951 Gaspra.4 Science performed by the Galileo Orbiter at Jupiter.2.4.2.2 Energetic Particles Detector (EPD).2.4.1.4 Photopolarimeter-Radiometer (PPR).2.4.1.3 Ultraviolet Spectrometer / Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (UVS/EUV).2.4.1.2 Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (NIMS).
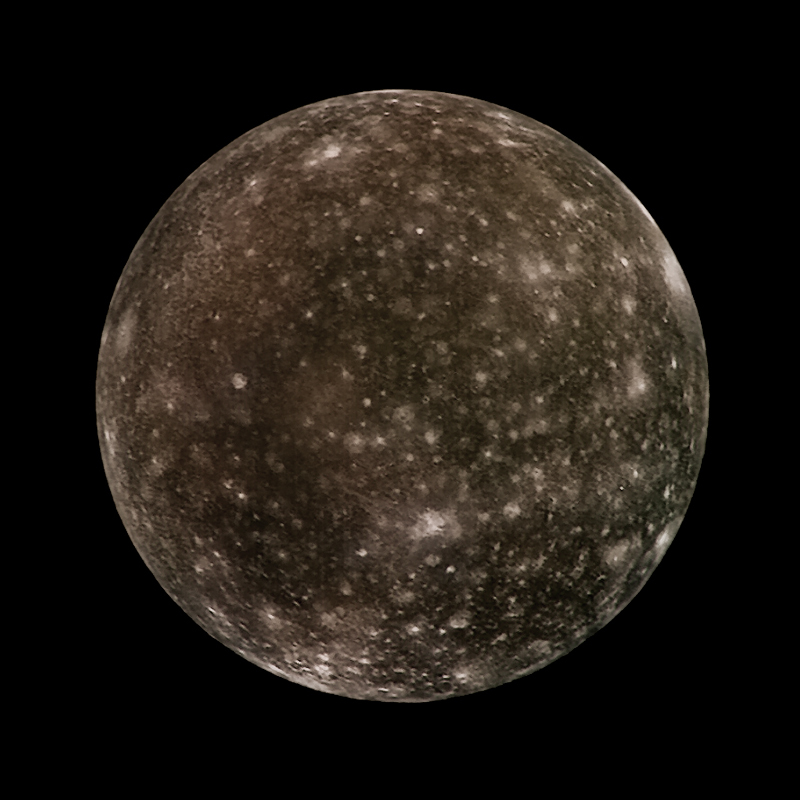
Of particular concern was the ice-crusted moon Europa, which, thanks to Galileo, scientists now suspect harbors a salt water ocean beneath its surface. On September 21, 2003, after 14 years in space and 8 years of service in the Jovian system, Galileo's mission was terminated by sending the orbiter into Jupiter's atmosphere at a speed of nearly 50 kilometres per second to avoid any chance of it contaminating local moons with bacteria from Earth. Galileo conducted the first asteroid flyby, discovered the first asteroid moon, was the first spacecraft to orbit Jupiter, and launched the first probe into Jupiter's atmosphere. It arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, a little more than six years later, via gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth. Named after the astronomer and Renaissance pioneer Galileo Galilei, it was launched on Octoby the Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-34 mission. Galileo was an unmanned spacecraft sent by NASA to study the planet Jupiter and its moons. Contributors are invited to replace and add material to make this an original article. The multispectral information provided by Galileo’s instruments was of particular interest.The content on this page originated on Wikipedia and is yet to be significantly improved. It provided clearer views of the lunar farside and the north and south polar regions. Galileo obtained information in new areas and with new instruments that helped clarify information gathered by other missions to the Moon. While Galileo observations of the Moon were brief, its instruments were still able to gather useful information. Most of the lunar hiqhlands appear red, indicating their low titanium and iron content. Dark purple patches (left center) mark the Apollo 17 landing site and are ancient explosive volcanic deposits. Titanium-rich soils, typical of the Apollo 11 landing site, appear blue, as seen in Mare Tranquillitatis (left side) soils lower in titanium appear orange, as seen in Mare Serenitatis (lower right). The images were processed to exaggerate the colors of the lunar surface for analytical purposes. This false-color image of part of the Moon was constructed from four images taken by Galileo’s imaging system as the spacecraft flew past the Moon on December 7, 1992.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
